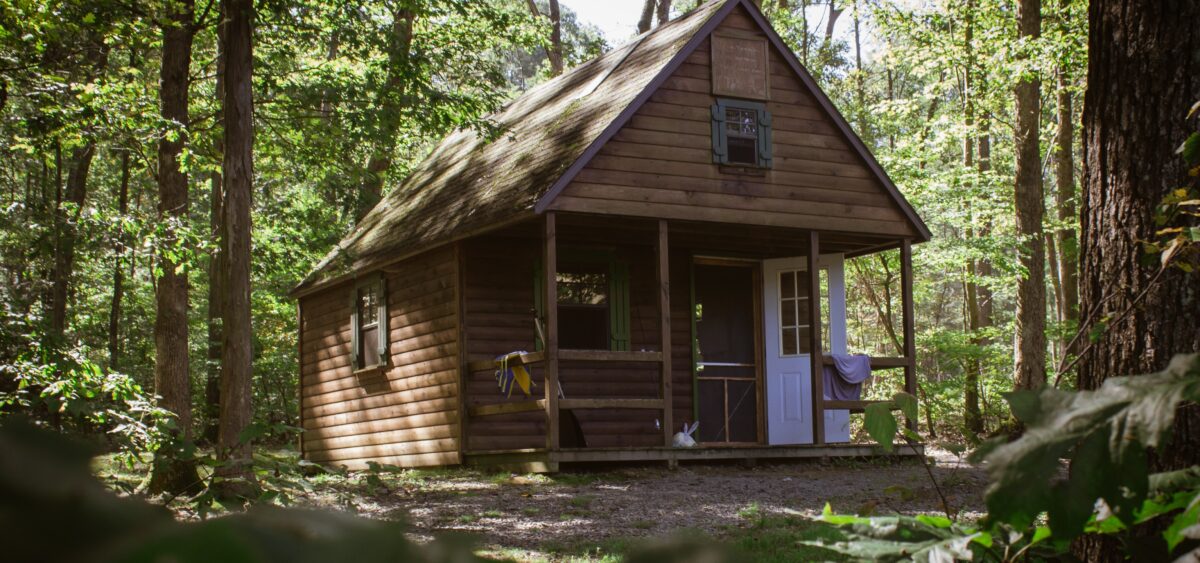
To write about silence—what a paradox. “When I pronounce the word Silence / I destroy it,” wrote Wisława Szymborska in The Three Oddest Words (translated by Stanisław Barańczak and Clare Cavanagh).
What could be said about silence except that there is less and less of it, just as there is less and less darkness (excessive nighttime lighting due to numerous sources of artificial light is the cause of the light pollution hindering astronomical observation of the sky, but it also interferes with the well-being of animals and plants adapted to living in darkness during the night)? In the civilized world, it is almost never completely dark—and never completely quiet. Like everything that is natural and rare, silence becomes an exclusive commodity—we leave the city to find ourselves away from its clamour, to wind down and rest. Silence is a luxury, being “out of reach” (with no access to the internet or a phone)—an extravagance few of us can afford, while there are fewer and fewer places where it is possible to really ‘cut oneself off’ from the world.
Portrait of Jeanne Hebuterne (Portrait de Jeanne Hebuterne) by Amedeo Modigliani, Barnes Foundation
My situation as I begin to write this piece: early morning